Complete Digital Marketing Dictionary
53 digital marketing terms defined
Digital marketing seems to have a language of its own. PPC, ad extensions, SEM, impression share, the list goes on and on. For anyone not well-versed in the digital marketing industry, all these terms and acronyms can get confusing, which is why we decided to create our own digital marketing dictionary.
This guide should help clear up some common terms around websites, search engines and general online marketing. Enjoy!
A
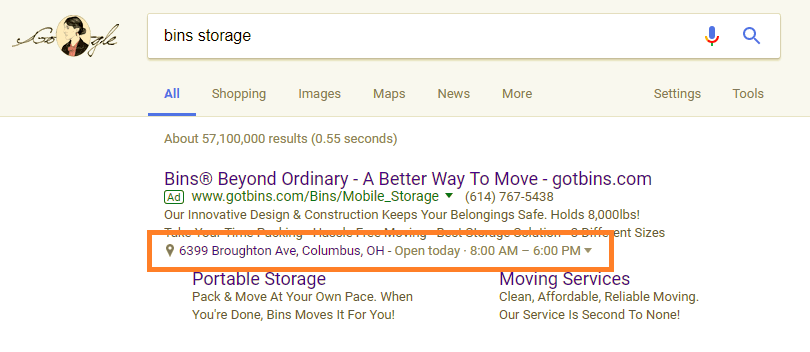
Ad Extensions : Additional information about a business that can be added to a paid ad on Google or Bing for free. This includes reviews, sitelinks, callouts, calls, locations and more. Ad extensions provide more information to users and expand the ad, taking up more space on a results page.
AdWords:
(See Google AdWords)
Algorithm:
A code or process that computers—or, specifically, search engines—follow to achieve a certain result. Algorithms tell search engines like Google how to rank websites and which results to show.
Alt Text:
Text that is added to HTML code to describe an image, which is used to provide information about an image for those who have a visual impairment, or when an image won’t properly load.
Average Position:
A metric that determines the average place a website ranks in a search engine result. There are 10 positions per page, with the first position being the top spot.
B
B2B (business to business):
A type of business that works primarily with other businesses.
B2C (business to consumer):
A type of business that works primarily with consumers.
Bing Ads:
The platform used by Bing for paid advertisements.
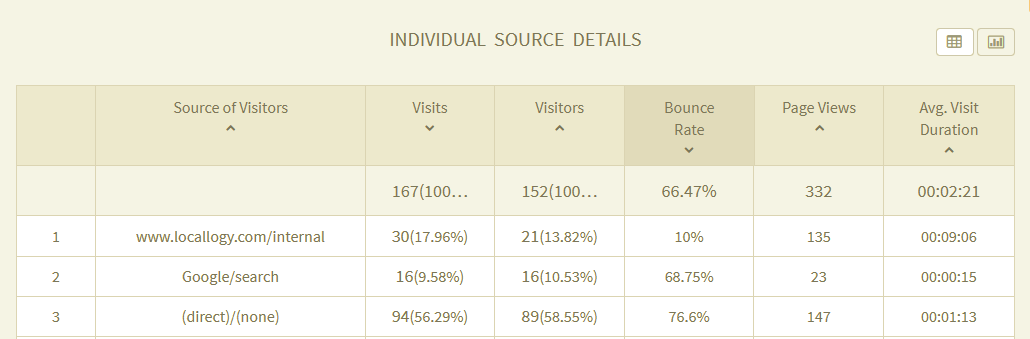
Bounce Rate:
The percentage of single page visits to a website. This is the rate at which people visit a web page and then immediately leave the website without going to any other pages.
C
Citation:
Any reference to a business on the internet. Citations typically include a link to the business’s website, address, phone number and other important information.
Content:
Any media on a website that provides information and adds value. This most commonly refers to text, but could also include photos, videos or graphics.
Conversion:
When a website visitor turns into a lead because they have made a purchase or contacted the business. (See Lead)
Conversion Rate:
The proportion of website visitors that turn into leads. This is measured by number of calls, emails and forms filled out on a site.
CPA (cost-per-acquisition):
The amount a business spends in advertising in order to gain a new customer. The equation for determining CPA is total spend divided by number of leads.
CPC (cost-per-click):
The amount a business pays when someone clicks on a PPC ad.
CTA (call-to-action):
Content that motivates visitors to take action toward a product or service immediately. CTAs usually give a reason why the person should buy in, and use phrases like “call now” or “add to cart”.
CTR (click-through rate):
A percentage that tells how many times an ad was clicked on, out of the amount of times it appeared.
D
Digital Marketing Campaign:
All online efforts that work together to market a website to a certain audience, using various methods such as SEO, PPC, local listings, social media and more. A digital marketing campaign combines all these elements with the goal of showing up in relevant search results.
Display Ads:
A form of advertisement that includes highly visual elements, such as photo, video and/or audio.
E
Email Marketing: The process of sending out targeted emails to a group of people in order to make a sale or get them to your website.
F
Facebook Advertising: The program offered by Facebook that allows advertisers to display ads targeted at users based on demographics and psychographics gathered by the social media platform.
G
Google AdWords:
The platform used by Google for paid advertisements.
Google Analytics:
A free program offered by Google that is used to track and analyze a wide variety of data about a website. Source of website traffic, conversions, bounce rate and much more can be tracked and compared during adjustable date ranges. Google Analytics is widely used by digital marketing professionals to study the effectiveness of online marketing efforts and make adjustments to achieve positive results.
Google My Business:
Google’s platform for business owners that allows them to control the information that appears for their businesses in search results. Information such as the official name, address, phone number, hours of operation, reviews and website links can all be managed from a GMB account, which plays a central role in local SEO campaigns.
H
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language): A coding language used by websites to tell a web browser what a page should look like.
I
Impression:
A measurement in PPC ads used to determine how many times an ad appeared in a search result.
Inbound link:
A link that comes to a website from a different website.
K
Keyword:
A key term or phrase that summarizes the most important information on a page and is crucial for SEO. Keywords tell search engines what the focus of a page is, and they are how users find the content they are looking for. When one performs a search, the term or phrase typed into the search engine is the keyword.
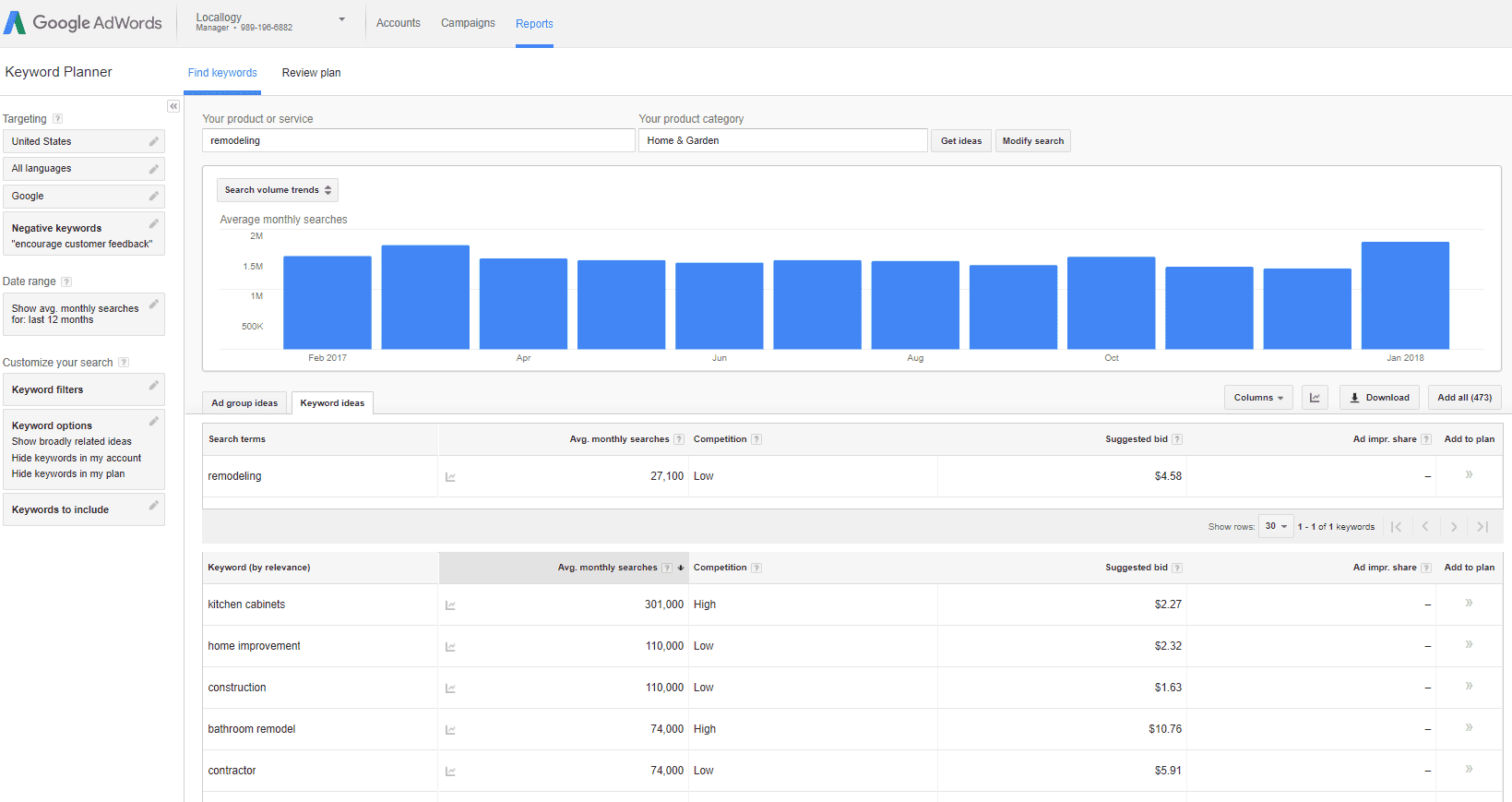
Keyword Planner:
A tool offered as part of Google AdWords that allows users to find the best keywords for their webpage. Keyword Planner shows data around how often the keyword is searched, the suggested bid for PPC campaigns and other metrics. This tool helps businesses find the right keywords to use in SEO content or paid ads.
L
Landing Page
: The page a user lands on after clicking a certain link.
Lead:
A consumer who turns into a potential customer because (s)he has contacted the business through email, phone or online form.
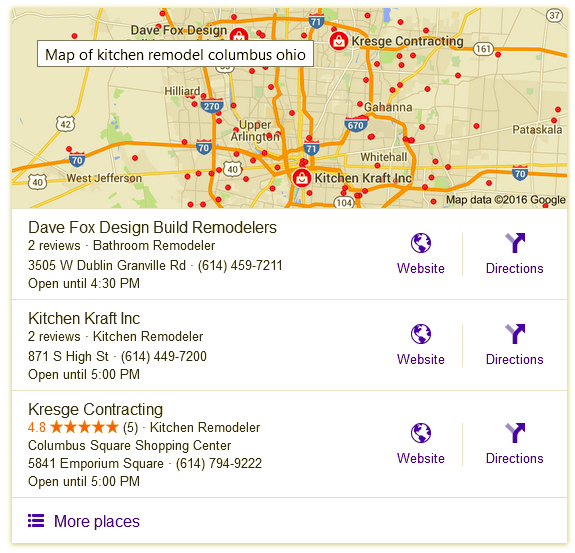
Local Pack/Local 3-Pack:
The top three local results displayed in Google search results. Google chooses the three best results based on keywords in relation to your location.
Longtail Keyword : Multiple keywords used together to form one longer phrase of keywords. These typically get less searches, but get more exact matches when users are looking for something highly specific.
M
Meta Description: The description of a webpage that accompanies a link to the page, and appears in various places, such as a search engine result. Meta descriptions help SEO by summarizing what’s on the page using keywords.
N
NAP (name, address, phone number)
: The information listed in local citations. It is crucial to local SEO that this information is correct on every local citation website, such as Google Business, Yelp, Houzz, etc.
Navigation:
The way users move from one page to another within a website.
O
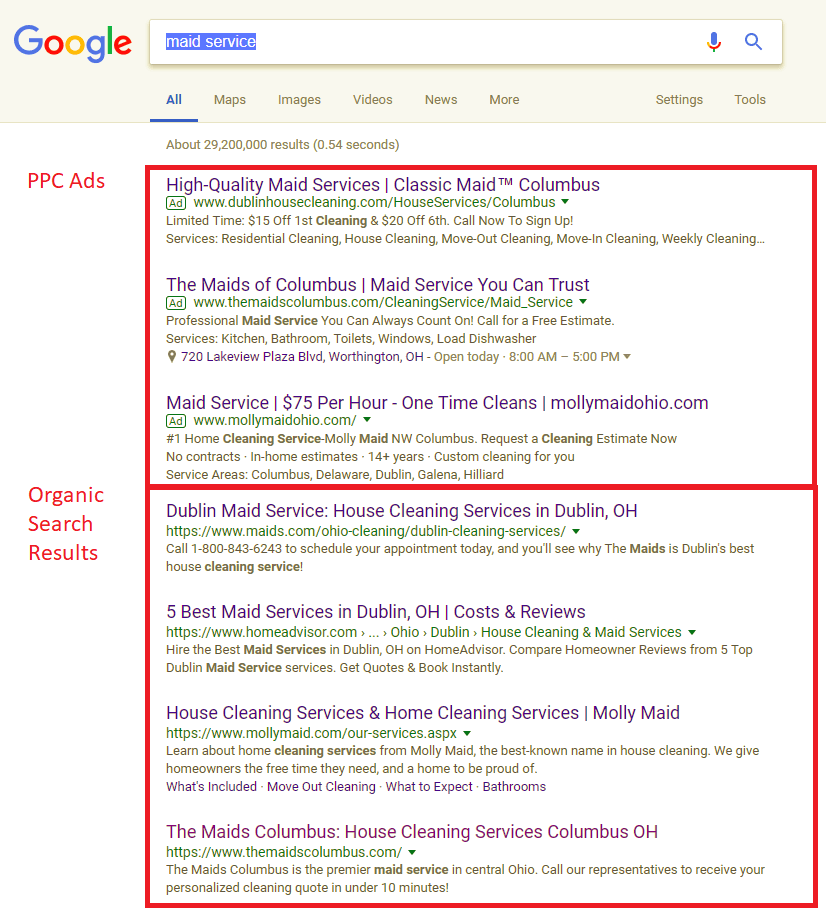
Organic Search Results : Websites shown by search engines that are deemed to be the best result for a search, not including paid advertising.
Outbound Link: A link that goes to a website to a different website.
P
PPC (pay-per-click): A paid advertising method that shows a website as an advertised result in a relevant search, and makes the business pay for every click its ad gets. PPC is commonly used with search engines like Google and Bing.
Q
QS (quality score): A rating system used by Google AdWords and Bing Ads, in which a paid ad is rated on a scale of 1-10 based on how well the campaign’s keyword, ad copy and landing page relevance align.
R
Rankings:
The term used to quantify where a website appears in search engine results. Rankings are based on how relevant a webpage is to the keywords used in the search, and can fluctuate over time.
Remarketing
: A type of paid advertising that shows specific ads to customers based on websites they’ve previously visited. The goal of remarketing is to get people back to a website if they left without converting into a lead.
ROI (return on investment):
The amount of money a business makes as a result of the money spent on marketing efforts.
S
Search Impressions Share:
The number of impressions an ad received divided by the number of times the ads were eligible to show.
SEM (search engine marketing):
Any form of digital marketing that involves the use of search engines and has the goal of showing up higher in rankings for either organic or paid results.
SEO (search engine optimization):
The process of enhancing areas of a website—such as content and coding—to improve the website’s performance in organic search engine results.
SERP (search engine results page):
The page of results that appear after performing a search on a search engine.
Source:
The various places from which traffic comes to a website (AKA the “source” of website traffic). Sources can include search engine, social media, blog posts and other websites.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer):
The standard security technology for establishing an encrypted link between a web server and a browser. An SSL certificate is needed to create a connection between a web server and a browser.
U
Unique Visitors:
A measurement used to see how many new users are coming to a website over a given time period, tracked by the individual’s IP address. Once a person has visited a website, all future visits will be counted as regular website visits.
UX (user experience):
How users interact with a website. This includes aspects like where they click, how they interact with content and how long they’re staying on pages. UX greatly influences how long people are on a website.
V
Visitors:
People who come to a website.
Voice Assistants:
A digital assistant that responds to voice-activated commands, performing a variety of tasks, such as playing music, checking traffic and using search engines to provide answers to user questions. Well-known voice assistants include Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa and Google Assistant. Voice assistants can be interacted with through devices like Google Home, Amazon Echo and HomePod, as well as smart phones, tablets and some computers.
Get the Latest Content in Your Inbox
Want to be the first to know about new content? Sign up to get our weekly blog posts sent to your email!